|
Advice article filter
|
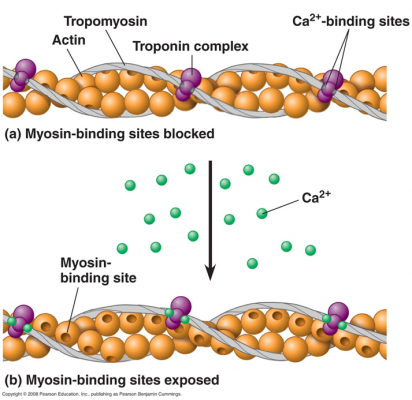
Nutrition and tips to build up your horses’ muscle quicklyBoth nutrition and training have a major influence on the functioning of the muscles. But how do muscles actually work? Which nutrients can influence this? And how can you give your horse extra support in building muscle? How do muscles work?When figuring out how muscles work and how you can stimulate muscle build, it is first important to know how muscles are built up. So here comes a small biology lesson: Muscles are attached to bone by tendons and are made up of fibres. These fibres are made up of proteins. A muscle is made up of thick and thin fibres. The thin fibres (actin) have a kind of imaginary opening and thus look a bit like an olive. There is a thread (tropomyosin) over these openings, that ensure that nothing can bind to the thin muscle fibres. These tropomyosin-threads are attached to each other via a complex: the troponin-complex. This complex keeps the tropomyosin-threads in its place. Under the influence of various complicated reactions, a message is left at the muscle cell via a nerve cell. This impulse ensures that calcium is released. The calcium ions then react with the troponin complex, causing the threads to shift. The openings that the threads covered are now exposed. Under the influence of an energy conversion from the muscle cell, protrusions of the thick muscle fibres (myosin) connect with the openings in the thin muscle fibres (actin). A similar system now arises as when a trailer is attached to a car. Due to various energy conversions, the thin muscle fibre (actin) shifts and this causes muscles to move. By re-binding with an energy molecule, the coupling between the thick and the thin muscle fibre is released, everything moves back into place, and the cycle can start again. Tips for extra muscle building in horsesIt is important to realize that a horse can never get more muscles; the amount of muscle cells is genetically fixed. But muscles can get thicker. Through training, muscle cells are stimulated to store more energy, so that the muscle mass increases and the performance and endurance of your horse will increase. Adjust protein when needed Proteins are the building blocks for muscles, actually for all tissues in the body. A common misconception is that horses that do not develop enough muscles must receive an overdose of proteins, while it is in fact very important to match the protein yield of your horse to its need. When protein is not used as a building material due to overdose, a horse uses it as energy. This is not exactly harmful, but it is also not very efficient. A surplus in protein is excreted by the kidneys as ammoniac, which can become a burden in the stable, for the environment and for horses with respiratory problems. The amount of protein your horse needs varies depending on the type of work or for example whether a horse is (or was) in foal. Read more about proteins in horse feed and the average requirement here. Training schedule for muscle building Training and condition play a crucial role in building muscle. It is important that the training is built up slowly and you keep plenty of variety. When a horse is in good condition, you increase the amount of energy sources in the muscle that ensures that your horse can work longer without acidifying. Tips for training:
Nutrition and supplements for muscle buildingProtein is an important nutrient that can contribute to muscle build up. Proteins also consist of small building blocks, called amino acids. There are both essential and non-essential amino acids. The Horses body can create non-essential amino acids, but not essential amino acids. A horse must get these through its diet. Essential amino acids for horses are:
The Pavo MuscleBuild supplement contains whey powder that is well known in the bodybuilding world, which contains a number of very important amino acids for muscle building. Vitamin D3 helps against muscle fatigue, while L-carnitine is added to improve energy conversion in the muscle cells. In addition, Pavo MuscleBuild contains the natural CellProtect antioxidants for neutralising free radicals. Free radicals are waste that is released when energy is burned. These substances can damage cells and tissues. Pavo MuscleCare, with β-alanine and vitamin E, contributes to muscle care. Pavo Eplus also does this but it is made up of vitamin E, vitamin C and selenium. How do you prevent muscle acidification?Movement is made possible by a collaboration between tendons, ligaments and muscles with muscles being the most flexible. When a horses training is built up very quickly, there is a chance that the muscles pull on the ligaments and tendons because they are less flexible. When a muscle has to work very hard, there is also a chance of acidification. Also, a muscle requires extra fuel during heavy exercise. Fuel has to be burned to produce energy. There are two types of combustion that can take place in a muscle cell: anaerobic metabolism (combustion without oxygen) and aerobic metabolism (burning with oxygen). The consumption of fuel produces waste and both types of metabolism give a different type of waste. Acidification only takes place when anaerobic metabolism occurs in the muscle and not when aerobic metabolism occurs. When a horse gains more stamina through training, the amount of anaerobic metabolism in the muscles reduces while aerobic metabolism increases. A product such as Pavo MuscleCare allows the horse to accelerate the breaking down and the removal of waste products. This allows the horse to sustain intensive work easier and for longer. Horses that are known to suffer from stiffness and muscle pain after exercise can benefit from Pavo MuscleCare. If you are unsure whether your horse is predisposed to muscle acidification after (heavy) labour, then you can give the supplement Pavo Eplus as a preventative. Muscle building in older horsesA horses’ body changes after 18 years of age. With our experience we have seen that older horses react well to a higher protein content diet, with special attention being paid to the quality of the protein. An older horse benefits from an extra protein source with high-quality proteins, which means that there needs to be enough essential amino acids in the roughage. It is important to provide digestible food in order to ensure that your older horse does not suffer from a deficiency. To adequately care for the muscles, you can add extra antioxidants, such as vitamin C and selenium. Pavo 18Plus in combination with Pavo SpeediBeet roughage is the complete diet needed for the daily care of your senior.
Pavo 18PlusKeeping your senior horse fit and healthy Pavo E'lyteElectrolytes for competition horses Pavo EplusFor supple muscles Pavo MuscleBuildSupports rapid build-up of muscles Pavo MuscleCareOptimum care for muscles Pavo SpeediBeetHigh-fibre, quick soaking beet pulp flakes |

